When it comes to cannabis cultivation, female cannabis plants have been known to steal the spotlight. They are pretty highly prized by growers and canna lovers for their ability to produce resinous buds packed with cannabinoids like THC and CBD. Unlike male cannabis plants, which primarily serve the purpose of pollination, female plants are the source of the potent flowers.
Female cannabis plants are more expensive to cultivate and buy because they require careful cultivation to avoid pollination and ensure the highest quality product. Growers invest heavily in feminized seeds or cloning techniques to maximize their yield of female plants. They also have to make sure that every plant contributes to the harvestable product.
Moreover, female plants are valued for their higher resin production, which means more cannabinoids and terpenes. This translates into stronger, more aromatic, and flavorful cannabis products. And while female plants have become a premium choice in the market, male cannabis plants also exist. But, what’s their purpose? We’re here to talk about the male vs. female cannabis plants and why one is better than the other.
Understanding Cannabis Genders
We’ve already established that the cannabis plant can be classified into two primary sexes:
- Male
- Female
Each sex has a specific role in the plant’s lifecycle and its contributions to cannabis production.
Male plants are responsible for pollinating the female plants. Female plants are the ones that produce the resinous buds that contain cannabinoids like THC and CBD. This is probably one of the biggest differences between the two, as it influences everything from cultivation practices to the potency and quality of the final product.
How to Identify Male vs. Female Cannabis Plants
So, how can you tell if your cannabis plant is male or female? Let’s find out.
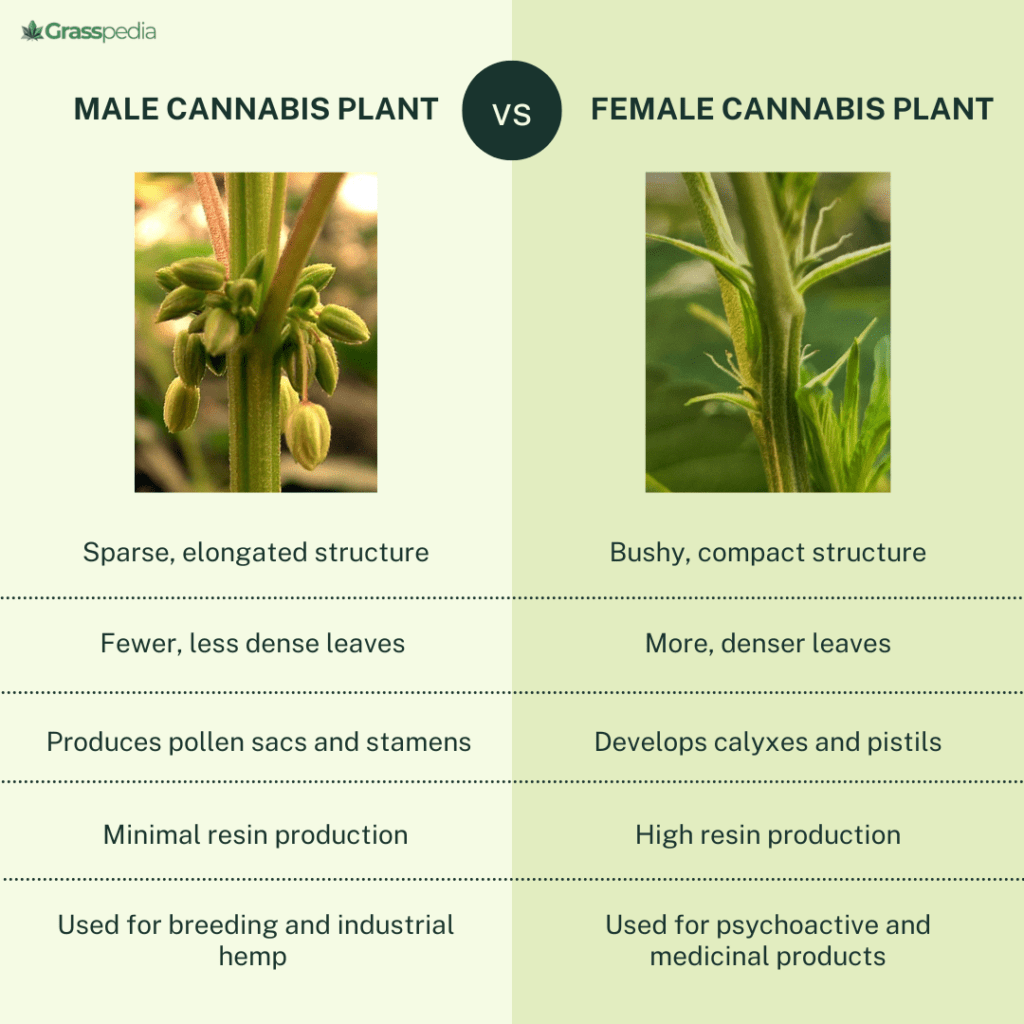
Physical Appearance
Male Cannabis Plants
- Height and Structure: Male cannabis plants are generally taller and less bushy compared to female plants. They have a more sparse and elongated structure.
- Fewer Leaves: Males have fewer leaves, and their foliage is less dense, which gives them an open appearance look.
- Pre-flowers: These appear after 3-6 weeks of germination and are typically small, round sacs that will eventually produce pollen. They tend to develop at the nodes where the stem meets the branches.
- Stamens: Male plants have stamens, which look like small, elongated stalks with a sac-like anther at the tip. The anther is where pollen is produced and released, often found within the pollen sacs.
Female Cannabis Plants
- Bushier Structure: Female plants are generally shorter and bushier than male plants. They have a more compact and dense growth pattern.
- More Leaves: They tend to have more leaves, and their foliage is denser. So, if you notice closely, they’ll appear fuller and more lush.
- Pre-flowers: Female pre-flowers are identified by the presence of pistils—small, hair-like structures that appear at the nodes.
- Calyx: Female plants have calyces, which are small, teardrop-shaped structures that form the base of the buds. The calyxes are covered in tiny, sticky trichomes and house the pistils, which look like hair-like structures that catch pollen.
Flowers
Male Cannabis Plants
- Pollen Sacs: The most distinctive feature of male plants is their pollen sacs. These small, ball-like clusters form at the nodes and, when mature, release pollen to fertilize female plants.
- Lack of Pistils: Unlike female plants, male plants do not develop pistils (the hair-like structures that collect pollen).
Female Cannabis Plants
- Buds: The most notable feature of female cannabis plants is their ability to produce buds. These resinous flowers are rich in cannabinoids like THC and CBD.
- Pistils: Female plants develop pistils that catch pollen from male plants. These hair-like structures are usually white or light-colored when they first appear and darken as they mature.
Growth and Maturity
Male Cannabis Plants
- Faster Maturation: Male plants tend to mature faster than female plants. This rapid growth allows them to release pollen early in the growing season to ensure successful fertilization.
- Less Resin Production: Males produce significantly less resin than females, which makes them less valuable for producing psychoactive products.
Female Cannabis Plants
- Slower Maturation: Female plants tend to mature more slowly than males. This gives them time enough to develop large and potent buds.
- High Resin Production: Females produce a significant amount of resin, which contains the cannabinoids and terpenes responsible for the plant’s effects and aromas.
Uses
Male Cannabis Plant
- Breeding: Although male plants don’t produce the high-quality buds that females do, they come in handy when breeding new cannabis strains. Male plants contribute genetic diversity, which lets breeders create hybrids with desired traits, such as higher potency, disease resistance, and unique flavors.
- Industrial Hemp: Male cannabis plants are often used in the production of industrial hemp, where their fibers can be utilized for making textiles, ropes, and other materials. While they’re not the focus of the recreational market, males are essential for maintaining a healthy and diverse cannabis gene pool.
Female Cannabis Plant
- Psychoactive Products: Female cannabis plants are harvested for their buds, which are used to produce a variety of psychoactive products, like dried flowers, bhang, oils, edibles, and concentrates.
- Medicinal Products: The high concentration of cannabinoids in female cannabis plants makes them a great use for medicinal use. They’re used to find relief from conditions such as chronic pain, anxiety, and inflammation.
Read more: Understanding Hemp: The Basics, Uses, and Legal Status in India
The Case of Hermaphrodites
Sometimes, cannabis plants can surprise you by being hermaphrodites, which ideally means that they possess both male and female flowers.
This condition can occur due to environmental stressors like extreme temperature fluctuations, light schedule issues, or genetic factors.
Hermaphroditic plants can self-pollinate, which can be a double-edged sword. While they can produce seeds, this can also result in lower-quality buds due to the presence of seeds in the harvest. For growers looking to cultivate high-potency flowers, hermaphrodites are usually seen as undesirable.
What’s the Learning?
So, this was it for male vs. female cannabis plants. Male plants, with their sparse structure and pollen sacs, play a key role in breeding and industrial hemp production.
Female plants, on the other hand, are valued for their dense foliage, high resin production, and ability to produce potent buds used in psychoactive and medicinal products.


